In today’s data-driven world, organizations collect massive amounts of data daily. Analyzing this data is crucial for gaining actionable insights, predicting trends, and making data-informed decisions. While traditional on-premise setups have been instrumental in large-scale data analytics, they present significant challenges as data volume and complexity grow. The shift to cloud computing has revolutionized data analytics, addressing these challenges and enabling powerful, scalable solutions.

Recently, we delivered a webinar on Cloud Computing for Large-Scale Data Analytics, covering its immense potential for businesses and demonstrating real-world use cases. For those who missed it, the slides are given below for the reference.
Now, we’ll see, Why data analytics? Is it useful in real world?
Large-Scale Data Analytics Use cases
- Customer Behaviour Analysis for E-commerce
- Real-Time Fraud Detection in Financial Services
- Supply Chain Optimization in Retail
- Sentiment Analysis and Brand Monitoring in Social Media
- Content Recommendations in Media & Entertainment
- Healthcare Insights : Process patient data to enhance diagnoses, personalize treatments, and improve outcomes.
We will focus on the stages of large-scale data analytics to achieve the most out of large amount of data.
The Stages of Large-Scale Data Analytics
Large-scale data analytics spans multiple stages, including data ingestion, storage, processing, analytics, machine learning, and visualization.
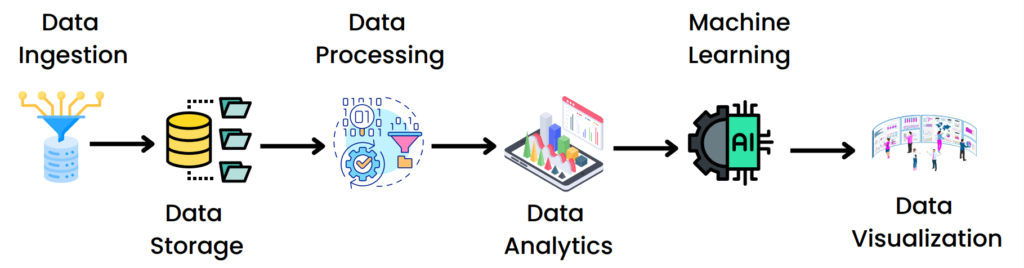
Each stage contributing to turning raw data into valuable insights:
- Data Ingestion: The process begins with collecting raw data from diverse sources, such as IoT devices, databases, logs, or external APIs, to prepare it for storage and analysis.
- Data Storage: Collected data is securely and efficiently stored using scalable storage solutions, ensuring easy access for processing and analysis.
- Data Processing: Raw data is transformed into a clean, structured, and usable format through techniques like filtering, aggregation, and normalization.
- Data Analytics: Processed data is analyzed to extract actionable insights using advanced tools, statistical methods, and algorithms.
- Machine Learning: Predictive models are developed, trained, and deployed to automate insights, continuously learn from data, and improve prediction accuracy.
- Data Visualization: Insights are translated into interactive visual formats such as charts, dashboards, and graphs to identify patterns, trends, and anomalies effectively.
Each stage plays a vital role in creating a comprehensive and impactful analytics pipeline, empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions. Data governance and security are crucial for managing and protecting large-scale data in the cloud at each of these stages.
Data Governance & Security: With tools like AWS IAM, KMS(key management service), and CloudTrail, organizations can ensure data privacy, integrity, and compliance while maintaining scalability.

Implementing best practices like role-based access, real-time monitoring, and data encryption allows businesses to securely harness cloud analytics, driving innovation and data-driven decision-making.
Next, we’ll explore why we migrate to cloud for data analytics.
Why Migrate to Cloud for Data Analytics?
While on-premise setups provide over resources, they face several challenges:
- Scalability Issues: As data volumes grow exponentially, scaling on-premise resources can be prohibitively expensive and time-consuming.
- Cost Challenges: Hardware upgrades, maintenance, and energy consumption add substantial costs.
- Performance Bottlenecks: Managing high-throughput data ingestion and real-time analytics often exceeds the capabilities of on-premise infrastructures.
- Integration Complexity: Connecting disparate data sources like IoT devices, social media, and enterprise systems requires extensive manual effort.
- Security and Compliance: On-premise systems demand significant investment in securing data and meeting regulatory requirements.
Cloud computing offers a dynamic, efficient alternative to on-premise solutions, empowering organizations with:
- Scalability on Demand: Easily handle growing data volumes without significant upfront investments.
- Cost Efficiency: Pay-as-you-go models and serverless technologies reduce operational costs.
- Global Accessibility: Access analytics infrastructure anytime, anywhere.
- Advanced Tools: Cloud platforms like AWS and Azure provide specialized tools for ingestion, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load), machine learning, and more.
- Integrated Security: Built-in encryption, identity management, and compliance tools ensure data safety.
Combining cloud computing with large-scale analytics allows businesses to seamlessly integrate data sources, analyze data in real-time, and uncover actionable insights faster than ever before. we will present the demos as blog series.
Future Blog Series Highlights
To build on this introductory blog, we’ll deep-dive into practical implementations and use cases of cloud-powered analytics in the following topics:
1. Mastering Data Transformation with AWS Glue and Querying with Athena
- Learn how AWS Glue simplifies data preparation by automating schema detection and cleaning.
- Discover how Athena makes querying large datasets seamless.
- Use case: How Glue and Athena work together to handle large-scale data stored in Amazon S3.
2. Simplifying Data Workflows: A Deep Dive into ETL
- Understand ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes and how they simplify data workflows.
- Tools like AWS Glue make ETL automation.
3. Real-Time Data Streaming with AWS Kinesis
- How Amazon Kinesis manages real-time data streams.
- Build a pipeline that processes live data and generates insights instantly.
- Use cases: Log monitoring, fraud detection, and real-time analytics.
4. Detecting Anomalies Using SageMaker and Kinesis: A Step-by-Step Guide
- It covers data generation techniques, training models with built-in algorithms, and deploying them as endpoints in Amazon SageMaker.
- Tools like Docker and Amazon ECR are used for containerizing models, while Kinesis handles real-time data streaming.
- AWS Lambda integrates data streams with SageMaker endpoints, and CloudWatch provides real-time monitoring of anomaly detection results.
Conclusion
Cloud computing and large-scale data analytics together transform how businesses manage and use data, offering scalability, flexibility, and real-time insights. This synergy unlocks innovation, enhances decision-making, and drives growth. Stay tuned for our upcoming blogs, where we’ll share real-world examples, practical tips, and the latest innovations in cloud-based analytics.

